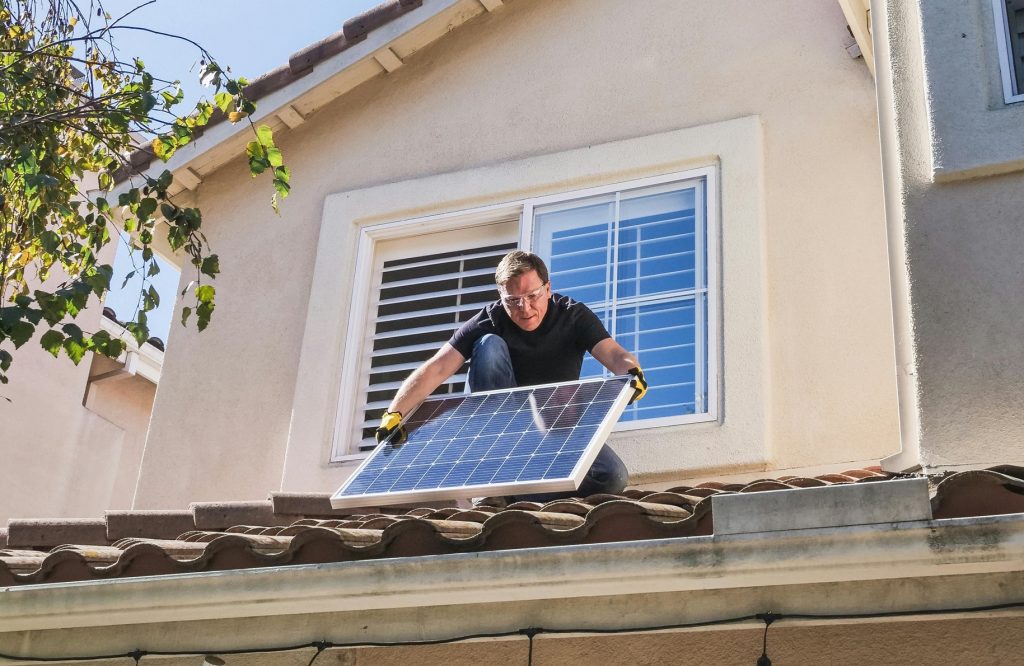
Distributed solar refers to the generation and supply of electricity from decentralised sources and in particular, electricity produced from residential rooftop solar power systems or solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. This differs from centralised electricity generation where a power plant generates electricity and distributes the power to consumers via an electricity grid.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), distributed solar has the potential to be a major contributor to the global transition to clean and renewable energy. Let us examine the how solar PVs can support our energy needs in the future.

Advantages of Distributed Solar
The typical solar PV system generates 1-25 Kilowatt-hour (kWh) of clean energy annually. With proper planning and installation, distributed solar provides benefits to asset owners and grid electricity generators and consumers.
Cost savings
A solar panel system can help owners save money; electricity generated from the solar panels reduces the amount of purchased electricity from the grid. The estimated break-even point for solar panel installations is from seven to ten years.
Less strain on electricity grid
Solar panel electricity helps to lighten the generation and transmission load on the grid, especially during peak demand. This ensures a more even distribution of electricity demand on the grid throughout the day, placing less strain on the grid and power plants.
Decreased impact of localised faults
With distributed solar power generation, localised faults will have lesser impact.
Contribute to a sustainable future
The energy from solar power generation is clean. Asset owners and consumers are thus reducing their dependence on fossil fuel power generation and playing their part to fight climate change.
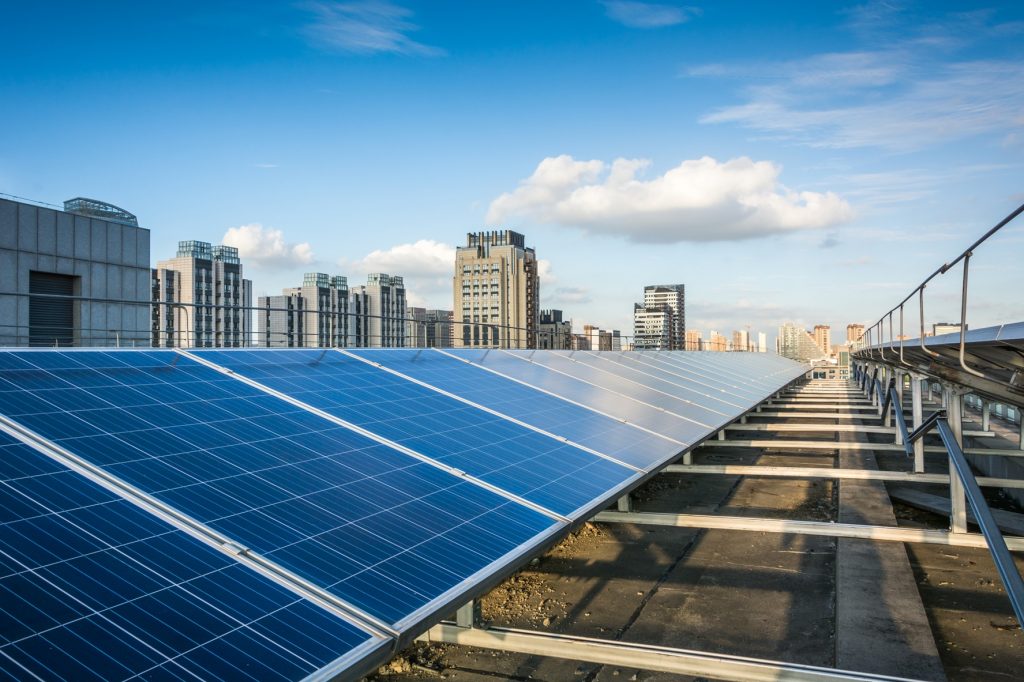

Demand and Growth of Distributed Solar
As per an IEA report, solar PV contributed nearly 375 GW – nearly three quarters – of renewable energy capacity addition in 2023. The growth of renewable energy capacity is forecasted to increase every year with solar PV capacity addition expected to reach 540 GW in 2028. This growth is driven by economic, regulatory, technological and environmental reasons.
Economic incentives
In most countries, solar PV is the least costly option for new electricity generation. Higher grid electricity prices are also pushing consumers to seek more cost-efficient alternatives. With the relatively low entry barrier and costs, Solar PV is looking more and more appealing.
Regulatory support
Large countries and regions are making efforts to promote solar PV.
- China added 100GW solar PV capacity in 2022. In addition, China’s 14th Five-Year Plan for Renewable Energy, released in 2022, sets ambitious targets for deployment, potentially driving further capacity growth in the coming years.
- The United States provided subsidies for solar PV installation in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) that came into law in 2022. Investment and production tax credits is expected to provide a significant boost to PV capacity and supply chain expansion.
- In response to the energy crisis in Europe, the European Union has accelerated solar PV deployment, adding 38 GW in 2022, a 50% jump compared to 2021. The Green Deal Industrial Plan and the REPowerEU Plan contains policies and targets that will drive solar PV investment in the coming years.
- Annual solar PV installation increased by more than 40% in 2022 to 18 GW in India. A new target to increase PV capacity auctioned to 40 GW annually and dynamic development of the domestic supply chain are expected to result in further acceleration in PV growth in the near future.
- Brazil doubled its annual solar PV installation to almost 11 GW in 2022. Deployment is expected to remain on this level in the foreseeable future due to demand for renewable energy from industry and electricity retailers.
Technological innovations
Crystalline silicon continues to be the dominant PV technology, with new, more efficient designs expanding their market shares. The shift to more efficient monocrystalline wafers accelerated in 2022, with the technology utilised in almost all crystalline PV production. At the same time, a more efficient cell design (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell [PERC]) is gaining popularity with almost 60% market share. Other new, even higher-efficiency cell designs (using technologies such as TOPCon, heterojunction and back contact) also saw expanded commercial production and captured about 35% of the market in 2022.
Environmental concerns
Beyond the political, economic and technological considerations, solar PV is gaining popularity because of increased consumer environmental consciousness. With growing awareness of the negative environmental effects of fossil fuels, electricity users are motivated to make consumption choices that seek to mitigate climate change. Installing solar PVs is one way to signal their concern for the environment.
REDEX and Distributed Solar RECs
Despite solar PV leading the renewable energy transition, the overwhelming majority of these assets are not registered with a renewable energy certificate registry. Solar PV owners, especially residential, are deterred by the manual, time-consuming and relatively costly process to register.
To resolve the above challenge, REDEX developed REConnect, a mobile app that provides solar PV owners with a simplified DIY registration process for their assets. With asset onboarding made convenient, solar PV owners can monetise their assets, recoup their installation costs faster and contribute to the global energy transition.
Whether you are a residential user or a business owner with solar infrastructure, signing up with REConnect enables you to generate income while actively promoting the use of renewable energy solutions. Start earning today!